What is Heat Transfer?
1. Heat transfer modes
Heat transfer is the energy transfer process as a result of temperature difference.
A thermal analysis is undertaken to predict temperatures and heat transfer within and around bodies. This information may then be used to model temperature dependent phenomenon such as thermally induced stresses or the effect on fluid flow in the case of a solidifying metal. Heat flow has been categorised into three different modes.
- Conduction
-
In a solid body, the energy is transferred from a high temperature region to a low temperature region. The rate of heat transfer per unit area is proportional to the temperature gradient in the normal direction. This mode of heat transfer is referred to as conduction.
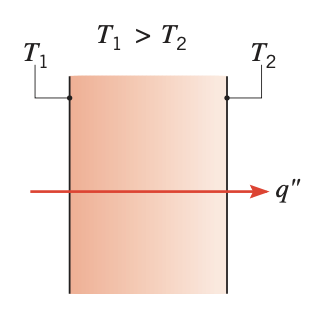 Figure 1. Conduction through a solid or a stationary fluid
Figure 1. Conduction through a solid or a stationary fluid - Convection
-
Convection heat transfer determines the heat flow between a solid body and the surrounding atmosphere of either gases or liquid. In the heat transfer literature, the term 'fluid' generally encompasses both gases and liquid. The convection heat transfer is either forced convection where the fluid is forced to flow around the solid body or natural convection where the fluid flow is due to density variations arising from the heat transfer process.
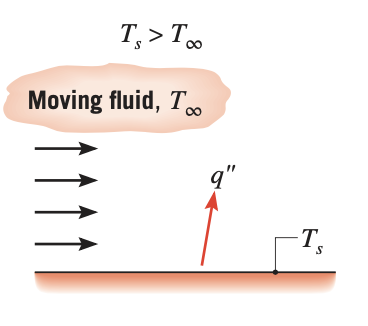 Figure 2. Convection from a surface to a moving fluid
Figure 2. Convection from a surface to a moving fluid - Radiation
-
In this mode of heat transfer, the heat flow can occur between a solid body and the surrounding atmosphere with or without the presence of gases or liquid. The heat flows by electromagnetic radiation. This means that heat flow can occur even if the solid body is kept in a vacuum.
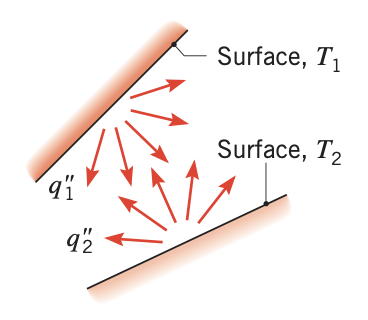 Figure 3. Net radiation heat exchange between two surfaces
Figure 3. Net radiation heat exchange between two surfaces
The heat conducted through a solid is convected as well as radiated from its surface to the atmosphere. The Figure below illustrates a particular case of this phenomenon. It is assumed that the temperature at the surface 1 is maintained at \(T_{1} K\) and is greater than the ambient temperature \(T_{\infty} K.\) As a result, the heat will conduct through the solid and dissipate into the atmosphere by the means of radiation and/or convection across the boundary surface 2.
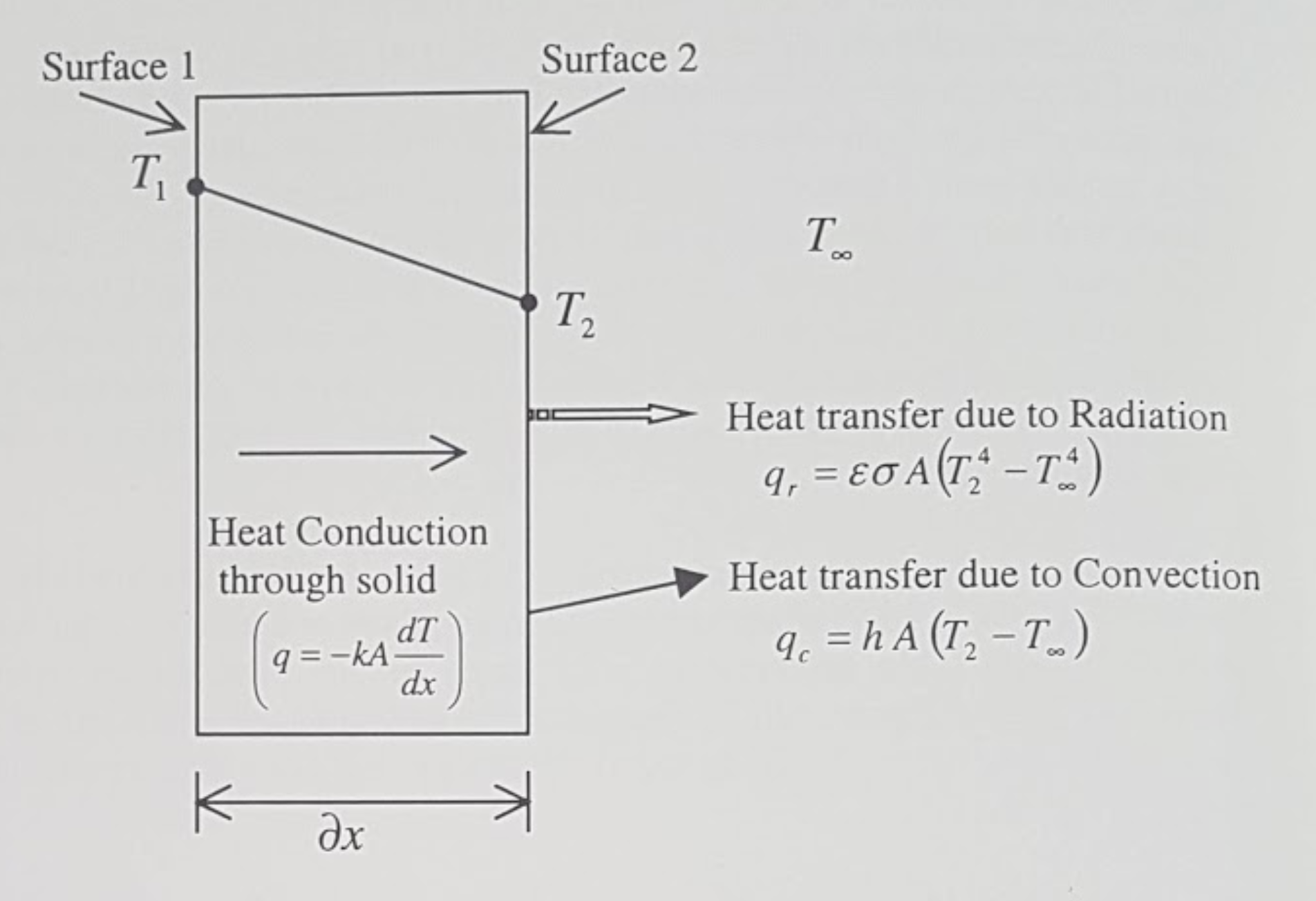
- \(q, q_{c}, q_{r}\)
-
Rate of heat transfer due to conduction, convection and radiation respectively \((W)\)
- \(A\)
-
Cross sectional area normal to heat flow (at surface 1 and } 2 \(\left(m^{2}\right)\)
- \(k, h, \varepsilon, \sigma\)
-
Conductivity \((W / m K),\) convection heat transfer coefficient \(\left(W / m^{2} K\right),\) emissivity and the Stefan Boltzmann constant \(\left(W / m^{2} K^{4}\right)\) respectively.
- \(T_{1}, T_{2}, T_{\infty}\)
-
Temperature at surfaces 1 and \(2,\) and the ambient temperature \((K)\) respectively \(\left(T_{1}>T_{2}>T_{\infty}\right)\)
From the modelling viewpoint, the conduction equation is numerically solved within a solid domain to determine the temperature variation.
Heat transfer due to radiation and convection occur only at the boundary of the solid and are, hence, included as boundary conditions.
The boundary of the solid may also be maintained at a fixed temperature or it may be insulated. Such identification of boundary conditions is necessary in order to solve the conduction equation.
2. Why thermal analysis?
There are many reasons for undertaking thermal analyses. In the context of engineering and in its simplest form, thermal analysis may be used to
- Estimate the temperature distribution within a component or assembly
-
This may be important where temperature is a key factor with regard to integrity or where differential thermal expansion causes internal stresses. Contrasting examples include microelectronic components that are subjected to a working load cycle and large structures that are subject to a fire risk.
- Calculate the temperature distribution in a component
-
it may be possible to establish heat flows that are present where energy transfer is a primary consideration (e.g. heat exchanger and condenser).
Thermal calculations are frequently coupled with other types of analysis:
-
fluid flow and
-
structural analysis.
2.1. Heat transfert and Structural Snalysis
The coupling of heat transfer and structural analysis comprises a common application: A structure or a material either contracts or expands when subjected to temperature changes.
The thermal contraction or expansion is directly proportional to the temperature changes and is characterised by a coefficient of linear expansion
where \(\Delta \varepsilon\) is the change in strain taking place in the body, \(\alpha\) is the coefficient of thermal expansion and \(\Delta T\) is the temperature change. The value of the coefficient of linear expansion is determined experimentally on very small samples and therefore represents an unrestrained system. However, in a structure, it represents initial strains in the body and can be converted into stresses and forces to be used as the load vector in the finite element structural analysis. In most practical applications, the contraction or expansion of the structure is partially or fully constrained thus inducing internal stresses. This can be important where thermally induced stresses may cause failure, where thermal distortion control is a requirement, or where residual stresses need to be evaluated in the case of components that are cooled (e.g. castings, heat treatment etc.).
2.2. Heat transfer and Other Physics
More complex systems also require thermal analysis:
- Chemical reaction
-
it must incorporate a model of thermal generation that arises as a consequence of the reaction.
- Phase change
-
Heat transfer with phase change has also become an important field because a large number of industrial applications (e.g. metal casting, plastics, injection moulding and other forming processes.) address this as part of a manufacturing process simulation. For example, the transient temperatures in a casting (or an injection moulded component) are important since they point to potential areas in the casting that may be defective, or they provide an indication of the duration of the cooling cycle.
3. Purpose of Thermal Analysis
Before an analysis is undertaken, it is important to establish the purpose of the investigation, since this motivates the study and defines some of the inputs and the output requirements from the analysis. * if temperature limits are a concern, then the temperature field throughout the system is the important output. * if the analysis goal is to establish cooling, then heat flux is likely to be more important and this will be displayed as an output.
| A good understanding of the underlying physical principles of the thermal analysis is a basic requirement for its correct application in any modelling task, in that the model must be 'fit for purpose'. |
The purpose of the analysis will also influence the input detail for the model. This is a key issue since this actually defines the thermal model. These details include the geometry, which may need to be abstracted from a design drawing or even from a sketch at the design feasibility stage, material properties and thermal boundary conditions. In the case of a transient thermal analysis this also requires the input of an initial temperature field together with time stepping information. This, similar to a structural analysis, the model input comprises abstracted geometry, material properties, constraints and loads.
The thermal analysis is classified into four categories. The classification is based on whether the heat transfer problem is time dependent and material properties or boundary conditions vary with respect to the temperature.
The simple flow diagram summarises the classification process.
Mode |
Mechanism(s) |
Rate Equation |
Transport Property or Coefficient |
Conduction |
Diffusion of energy due to random molecular motion |
\(q_{x}^{\prime \prime}\left(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m}^{2}\right)=-k \nabla T\) |
\(k(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K})\) |
Convection |
Diffusion of energy due to random molecular motion plus energy transfer due to bulk motion (advection) |
\(q^{\prime \prime}\left(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m}^{2}\right)=h\left(T_{s}-T_{\infty}\right)\) |
\(k(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m}^2 \cdot \mathrm{K})\) |
Radiation |
Energy transfer by electromagnetic waves |
\(\begin{aligned} q^{\prime \prime}\left(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m}^{2}\right) &=\varepsilon \sigma\left(T_{s}^{4}-T_{\mathrm{sur}}^{4}\right) \\ \text { or } q(\mathrm{W}) &=h_{r} A\left(T_{s}-T_{\mathrm{sur}}\right) \end{aligned}\) |
\(\begin{aligned}\varepsilon\\ h_{r}\left(\mathrm{W} / \mathrm{m}^{2} \cdot \mathrm{K}\right)\end{aligned}\) |
 .pdf
.pdf