Radiative cavity examples
We simulate radiative heat transfer in 2d and 3d closed cavities. The results of our computations are tested against literature results.
|
The following tests have been carried out using Newton’s non-linear iterations applied to the non-linear radiative boundary condition (see the heat toolbox documentation for more details on the formulation). Particular care has been put into the generation of the geometries in order to be as close as possible to the literature examples: small volumes of insulating material are inserted in correspondence of the junctions between the different materials in order to avoid heat trasfer through conduction. |
1. Rectangular cavity
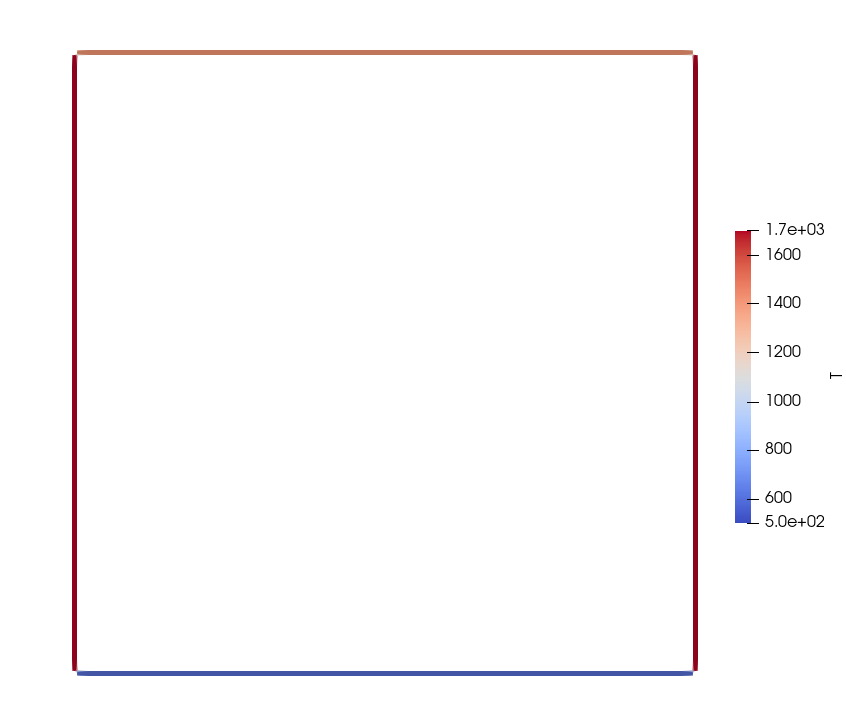
This example is taken from [Discontinuous_fem]. It consists in the simulation of the steady state of a rectangular cavity whose surfaces are kept at constant temperatures. The test requires to evalate the net radiative heat flux that leaves each surfaces.
1.1. Geometry and setup
The geometry consists in four rectangles of highly conductive material. They are mutually isolated by small regions of thermal insulator in correspondence of the corners of the cavity.
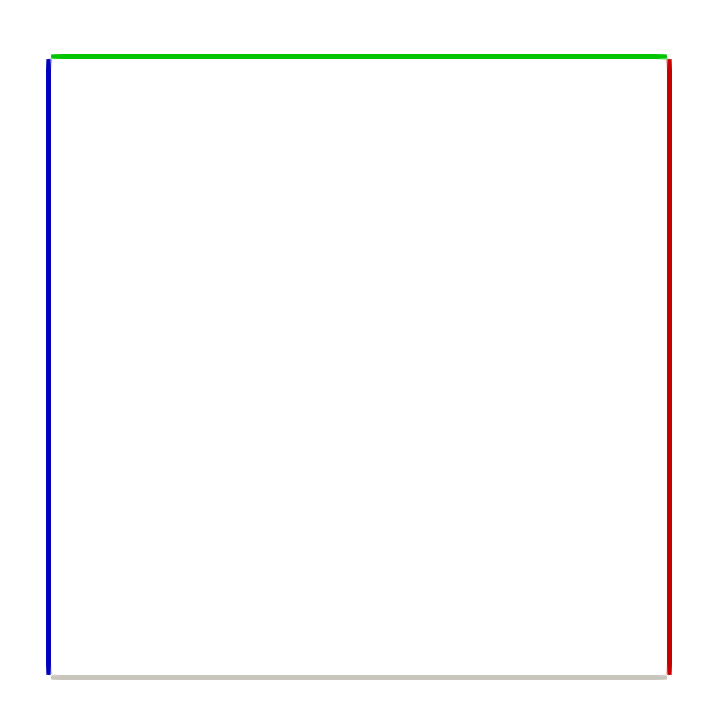
The required temperatures are imposed as Dirichlet boundary conditions on the external surfaces of the rectangles which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces of the rectangles.
1.2. Parameters and results
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
Heat conductivity rectangles \(k\) |
1400 |
Heat conductivity insulation \(k\) |
0.01 |
Temperature top wall |
1400 |
Temperature side walls |
1700 |
Temperature bottom wall |
600 |
Emissivity \(\epsilon\) |
0.5 |
Length cavity wall \(L\) |
3 |
Name |
Value |
Flux top wall |
35767 |
Flux side walls |
-97403 |
Flux bottom wall |
159040 |
2. Triangular cavity
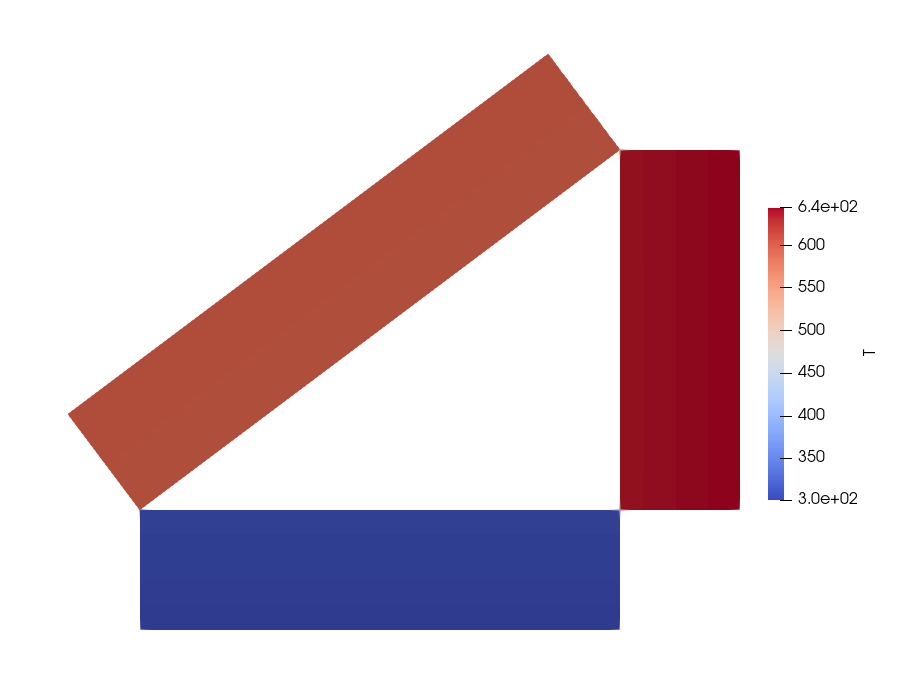
This example is taken from [Comsol]. It consists in the simulation of the steady state of a triangular cavity where heat flux and temperature boundary conditions are imposed. The test requires to evalate the net radiative heat flux and temperatures on the surfaces of the cavity.
2.1. Geometry and setup
The geometry consists in three rectangles of highly conductive material. They are mutually isolated by small regions of thermal insulator in correspondence of the corners of the cavity.
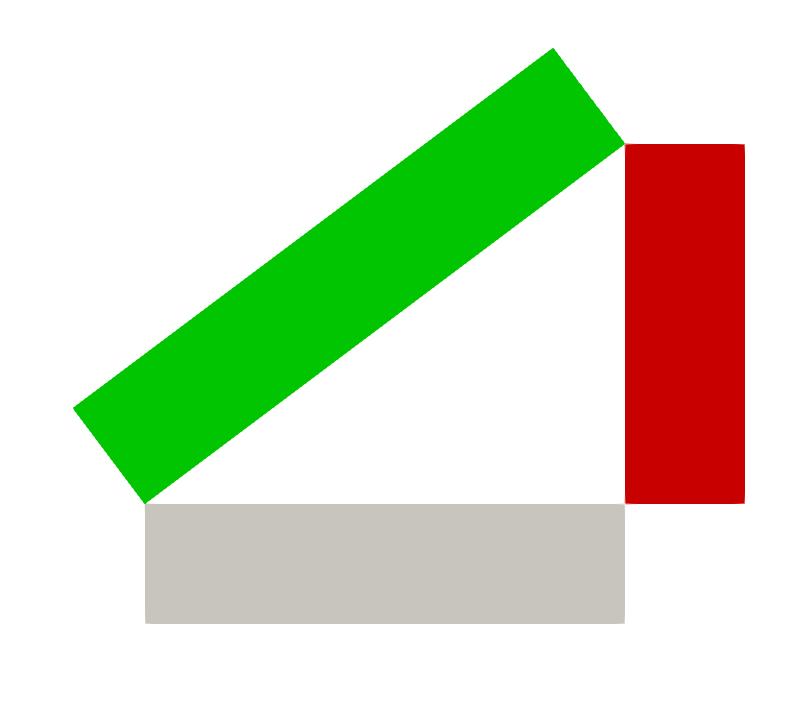
The required temperatures (fluxes) are imposed as Dirichlet (Neumann) boundary conditions on the external surfaces of the rectangles which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces of the rectangles.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
Heat conductivity rectangles \(k\) |
400 |
Heat conductivity insulation \(k\) |
0.01 |
Flux top rectangle |
-2000 |
Flux side rectangle |
-1000 |
Temperature bottom rectangle |
300 |
Emissivity top surface \(\epsilon\) |
0.4 |
Emissivity side surface \(\epsilon\) |
0.6 |
Emissivity bottom surface \(\epsilon\) |
0.8 |
Name |
Value |
Temperature top wall |
641 |
Temperature side wall |
600 |
Flux bottom wall |
-2750 |
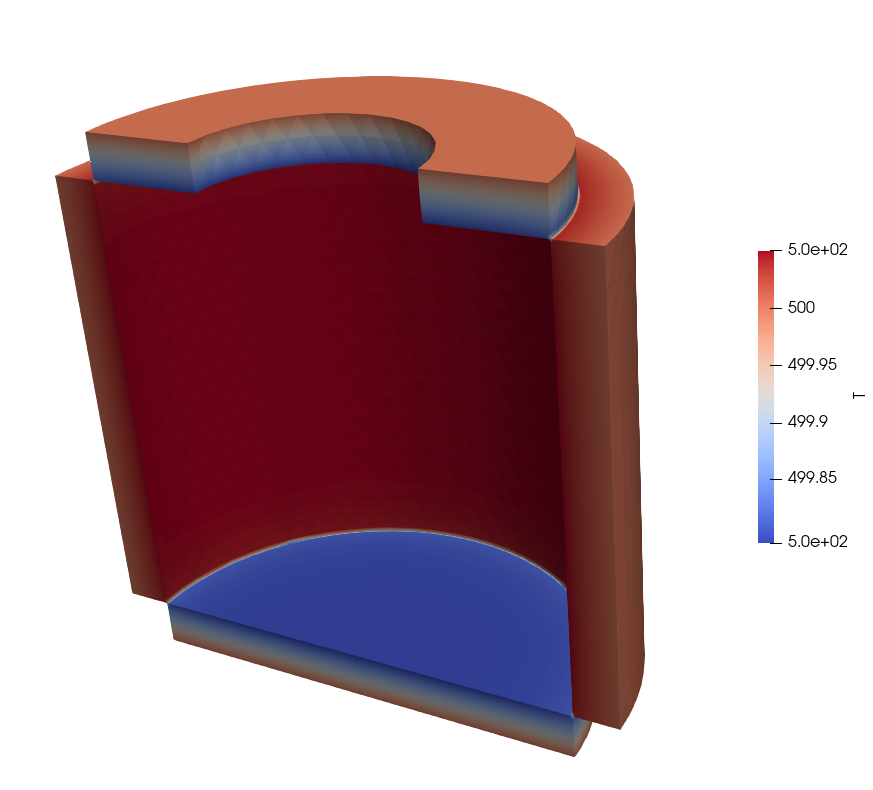
3. Cylindrical cavity
This example is taken from [Radiative_heat_transfer]. It consists in the simulation of the steady state of a cylindrical cavity whose surfaces are kept at constant temperatures. The test requires to evalate the net radiative heat flux that leaves the hole on the top of the cavity.
3.1. Geometry and setup
The geometry consists in three cylinders/annuli of highly conductive material. They are mutually isolated by small regions of thermal insulator in correspondence of the corners of the cavity.
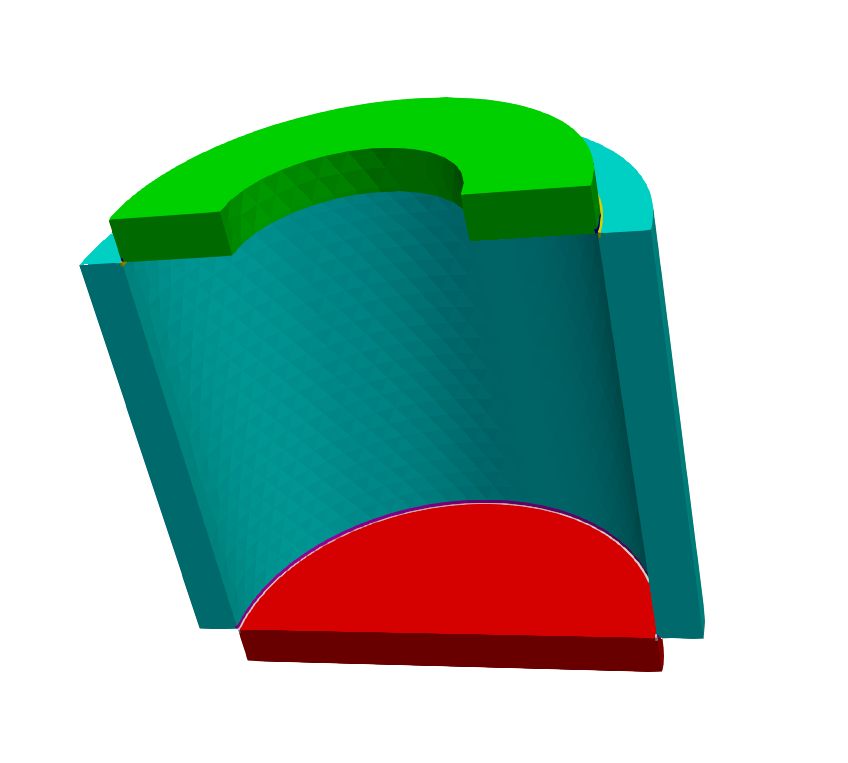
The required temperatures are imposed as Dirichlet boundary conditions on the external surfaces which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces.
3.2. Parameters and results
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
Heat conductivity rectangles \(k\) |
1400 |
Heat conductivity insulation \(k\) |
0.001 |
Temperature external walls |
500 |
Emissivity \(\epsilon\) |
0.5 |
Cavity diameter |
0.5 |
Top hole diameter |
0.25 |
Height of the cavity |
1 |
Name |
Value |
Flux through hole |
88.593 |
4. Bibliography
[Radiative_heat_transfer] Modest, M.F., Radiative Heat Transfer, Elsevier Science (2013) doi.org/10.1016/C2010-0-65874-3
[Discontinuous_fem] Ben Q. Li, Discontinuous Finite Elements in Fluid Dynamics and Heat Transfer, Springer (2006) doi.org/10.1007/1-84628-205-5
[Comsol] Radiation in a cavity, COMSOL Multiphysics documentation doc.comsol.com/5.6/doc/com.comsol.help.models.heat.cavity_radiation/models.heat.cavity_radiation.pdf
 .pdf
.pdf