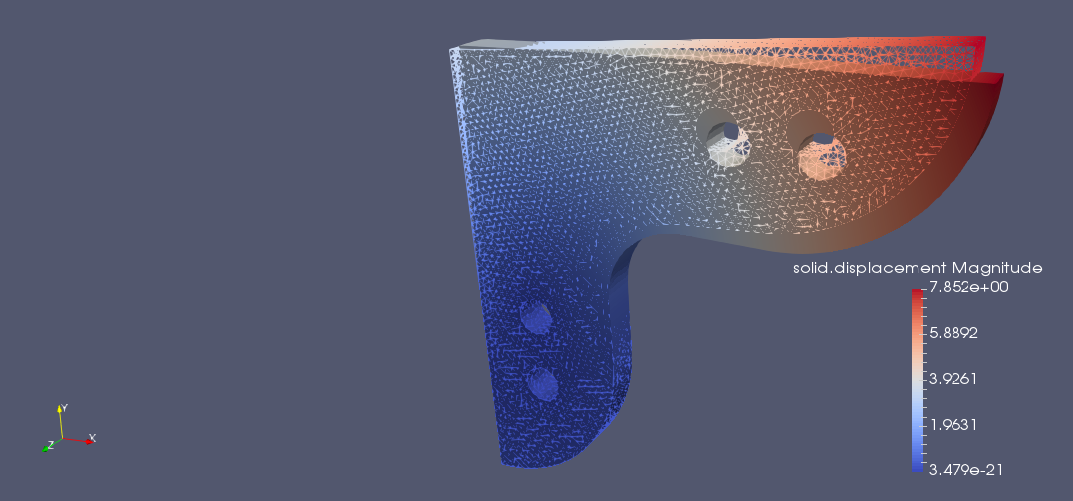
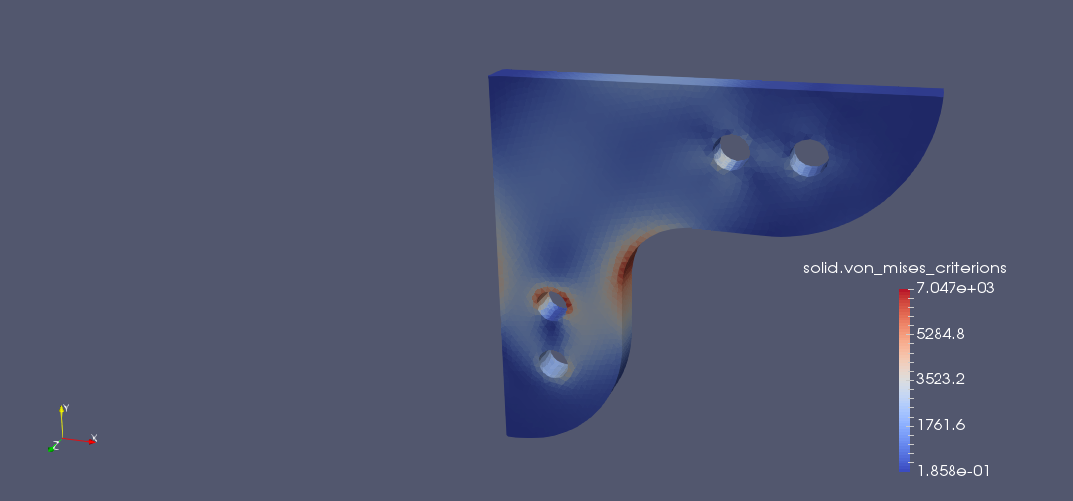
Effect of sheet rounding
1. Introduction
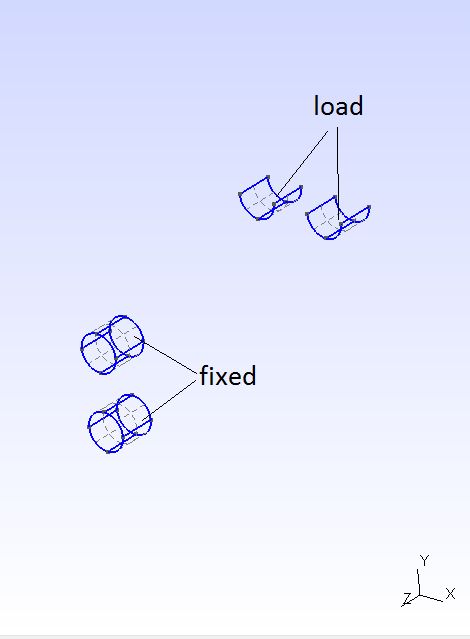
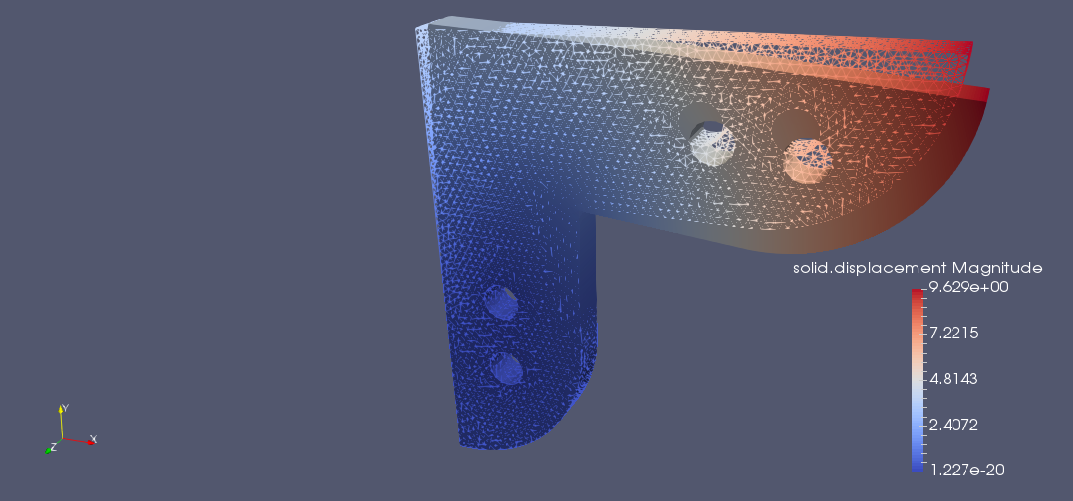
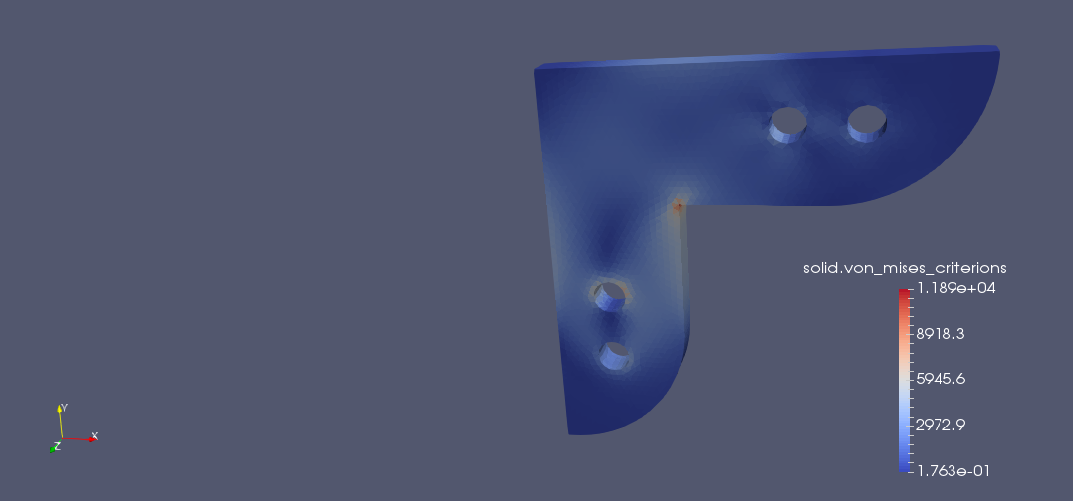
The 10 mm thick steel gusset plate shown has four identical embossed bolt holes. The inside perimeters of the two lower holes are completely fixed against displacement. The bolt load acting downward on the upper holes bears on the lower hal fon the inside edge of the hole. Determine the deformation and stress of the gusset plate. Check the effect of the rounding.
2. Model/Geometry
| First, we need to build the model, which we are going to do using the Gmsh-software. |
The finished original geometry and the meshed model with 2 mm mesh-size:
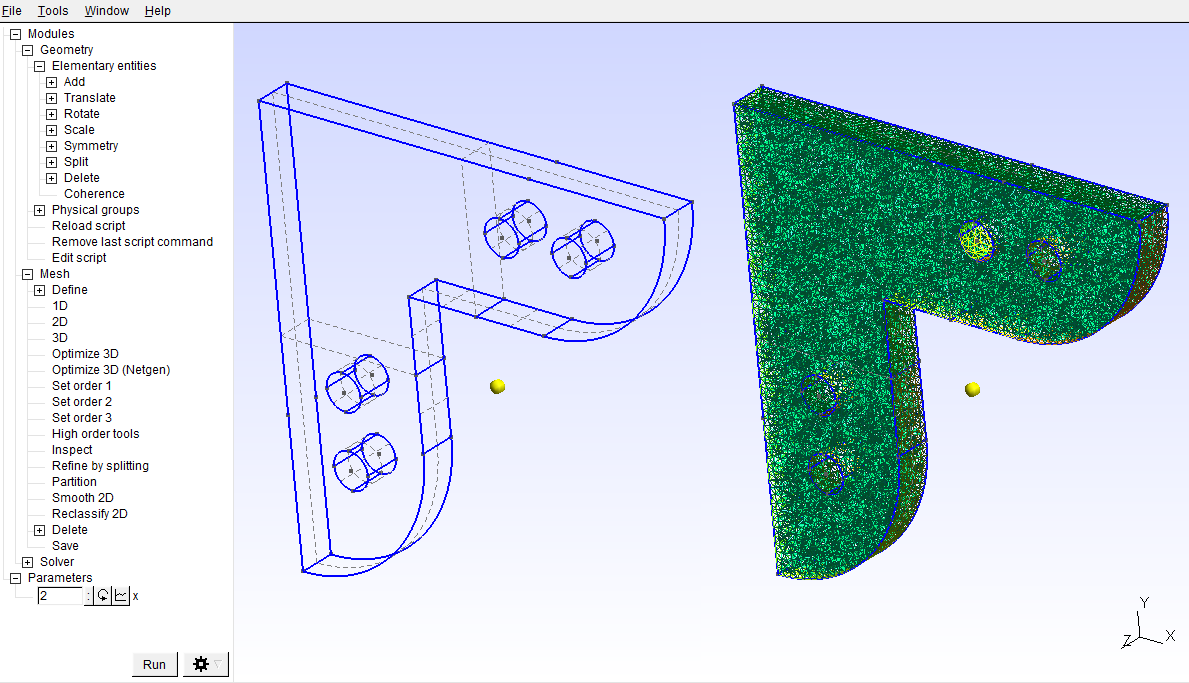
 .pdf
.pdf