Initializing Feel++
The core module provides the basic data structures to
-
setup and run Feel++ application in a parallel environment.
-
handle the command line options
-
download and upload data from and to Github and/or Girder
1. Setting up the Feel++ Environment
To set Feel++ environment, we create an environment and set the associated repository for the results.
A Feel++ environment can be created only once.
The repository can be global with respect to $HOME/.feelppconfig globalroot setting or local with respect to the current directory.
import feelpp as fpp
import sys
app = fpp.Environment(["myapp"],config=fpp.localRepository(""))Results
[ Starting Feel++ ] application myapp version 0.1 date 2022-Nov-04 [feelpp] create Feel++ root repository: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb [feelpp] create Feel++ geo repository: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/geo [feelpp] create Feel++ results directory: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/np_1 [feelpp] create Feel++ expressions directory: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/exprs [feelpp] create Feel++ logs directory: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/np_1/logs . myapp files are stored in /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/np_1 .. logfiles :/scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/np_1/logs
print("pid:",app.worldComm().localRank() )
print("isMasterRank:",app.isMasterRank() )
print("is parallel: ",app.isParallel() )Results
pid: 0 isMasterRank: True is parallel: False
2. Downloading data
Feel++ can query data on GitHub and Girder.
readme=fpp.download( "github:{repo:feelpp,path:README.adoc}", worldComm=app.worldCommPtr() )[0]
print("downloaded Feel++ README.adoc from Github: ",readme)Results
downloaded Feel++ README.adoc from Github: /scratch/jupyter/feelppdb/downloads/README.adoc
The code will get the file README.adoc from the toplevel Feel++ github directory downloaded
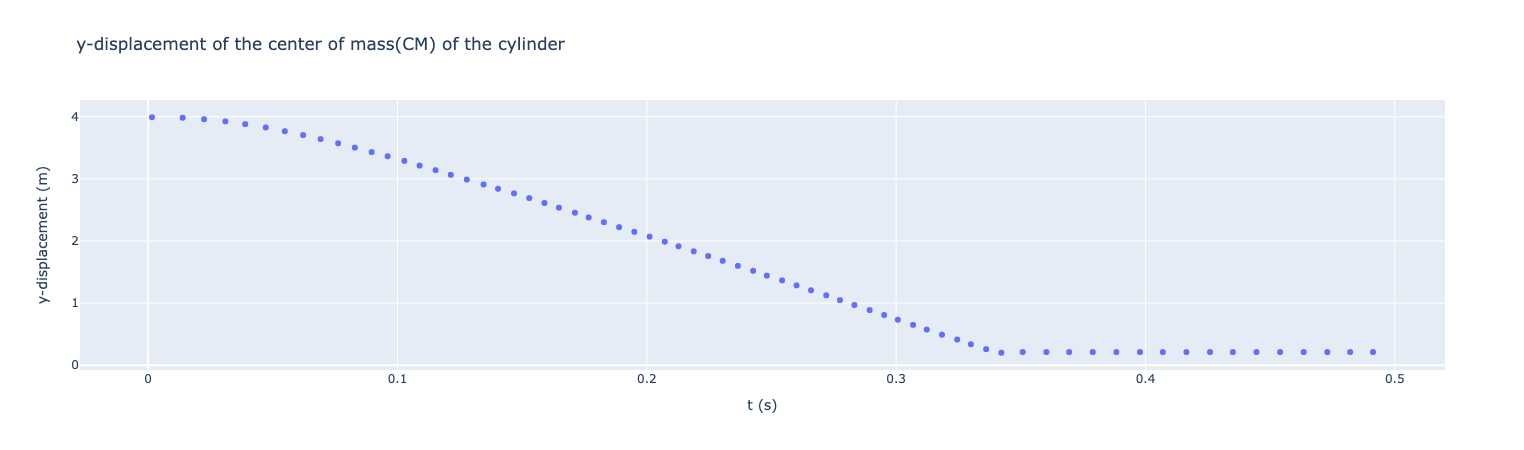
A bit more interesting example: the following code will download a csv file from the Feel++ github repository and plot the data using the plotly library.
acsv=fpp.download( "github:{repo:feelpp,path:toolboxes/fluid/cases/moving_body/gravity/cylinder_under_gravity/curve_comparison.csv}", worldComm=app.worldCommPtr() )[0] (1)
import pandas as pd (2)
df = pd.read_csv(acsv, sep=",") (3)
df.columns = df.columns.str.replace(' ', '')
print(df.head())| 1 | download the file curve_comparison.csv from the Feel++ github repository toolboxes/fluid/cases/moving_body/gravity/cylinder_under_gravity/curve_comparison.csv |
| 2 | use the pandas library to read the csv file |
| 3 | read the csv file and remove the spaces in the column names |
Results
TIME Y_CM 0 0.001538 3.991736 1 0.013846 3.983471 2 0.022432 3.959772 3 0.030984 3.925082 4 0.038925 3.881016
We can now use plotly to plot the data
import plotly.express as px
fig = px.scatter(df,x="TIME", y="Y_CM", title="y-displacement of the center of mass(CM) of the cylinder",labels={"TIME":"t (s)","Y_CM":r'y-displacement (m)'})
fig.show()Results
 .pdf
.pdf
 .ipynb
.ipynb